BST SẢN PHẨM MỚI
![]()
3.326.000 đ – 3.605.000 đ
Topper
270.000 đ – 285.000 đ
3.375.000 đ
3.625.000 đ
BST DOLL’S BEDDING
![]()
- CHĂN GA
- NỆM
- PHỤ KIỆN CHĂM SÓC GIẤC NGỦ
BST NỆM CAO CẤP
![]()
- NỆM FOAM
- NỆM BÔNG ÉP
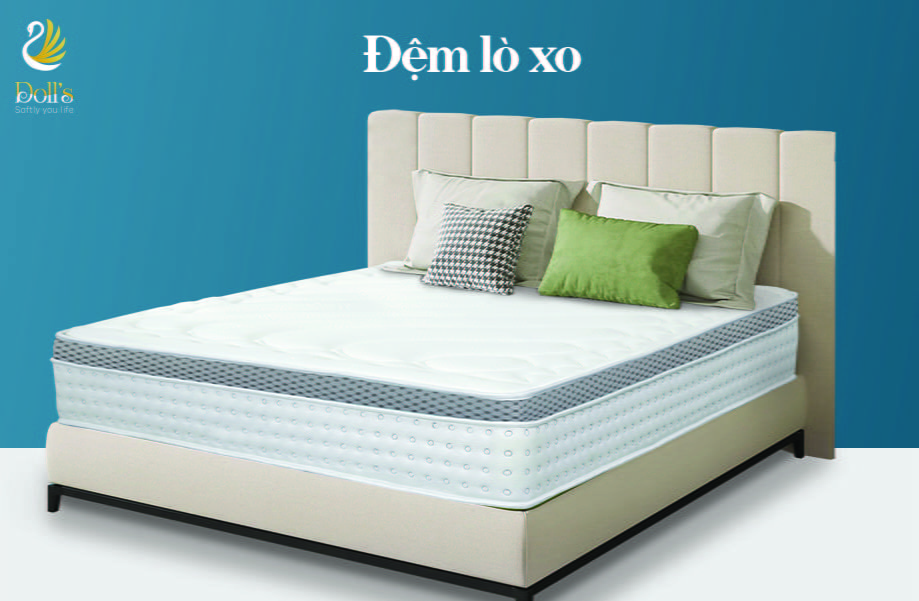
- NỆM LÒ XO
BST CHĂN GA CAO CẤP
![]()
EGYP | TENCEL | COTTON
Upload Image...
Upload Image...
Upload Image...
Upload Image...
KHÁCH HÀNG NÓI GÌ VỀ DOLL’S BEDDING
%3431739071408481%